full article:
Dear Editor
Post-supply contamination of tested fecal-free drinking water has been documented1. As such, in areas where improved drinking water sources are available, water deterioration following catchment is of concern. A study on water deterioration in rural Honduras linked fecal-contaminated fingertips and water containers to an immediate deterioration in water quality upon filling2.
In the article 'Water sanitation, access, use and self-reported diarrheal disease in rural Honduras' a questionnaire completed by 263 randomly selected adults attending a June 2011 medical brigade revealed differences in the examined variables between the geographically distinct communities of Coyoles, La Hicaca, and Lomitas located in the rural Department of Yoro area of Honduras3. Unpublished data from this same study was analyzed to evaluate the sanitation of containers for water transport and storage, use of lids on containers, and hand washing prior to container filling between these same communities. P values were computed to determine significant differences both between variables (when all responses from all surveyed individuals were considered) and communities using the three-way χ2 and Fisher's exact tests.
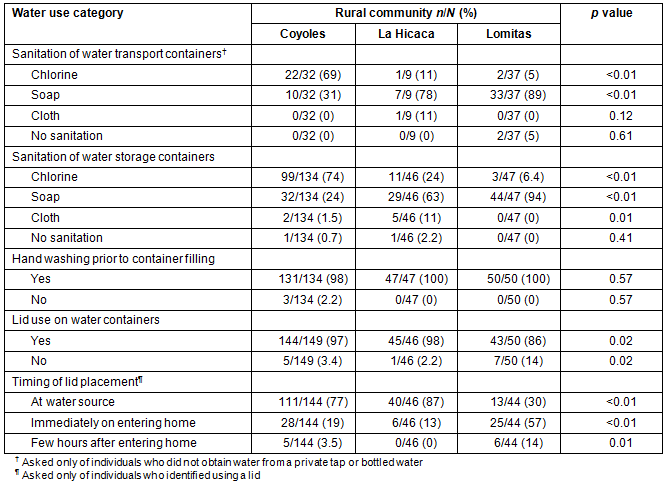
Table 1 summarizes sanitation and lid-use practices in each of the three communities. Chlorine was used to sanitize water transport and storage containers respectively by 32% (25/78) and 50% (113/227) of all surveyed individuals in the Department of Yoro (p<0.01). Chlorine use was most common in Coyoles, while soap was most common in La Hicaca and Lomitas. Less than 3% of all respondents identified not using any sanitation method on water containers (p<0.01). Washing of hands with soap and water prior to filling water containers was relatively constant, with greater than 98% of individuals in each community reporting this practice (p=0.57). About 95% (232/245) (p<0.01) of all participants identified using a lid on their water containers, with the Lomitas community being the least likely to identify its use (43/50, 86%) (p=0.02). Most individuals (164/234, 70%) (p<0.01) first placed a lid at the water source site. The Lomitas community had the largest amount of respondents placing the lid immediately upon entering the home (25/44, 57%) (p<0.01).
Our data indicate that significant and varied opportunities for improving post-supply water handling exist among these three geographically proximal yet distinct communities in rural Honduras. WHO recommends water safety plans as the most effective means of ensuring safe drinking water. Water safety plans endorse a holistic approach to water sanitation that involves comprehensive risk assessment and management of individual water systems throughout all steps in water supply, from collection to consumer4. Water safety plans have been shown to decrease community water supply system microbial growth and incidence of diarrhea5. In areas where water deterioration is of concern, WHO recommends the use of household water treatment technologies. These tools remove microbial pathogens from water at the home or point of use4. Our data suggest that water safety plans may optimize water handling in rural communities because they consider local needs and resources. Furthermore, household water treatment technologies may offer a solution to water sanitation in rural areas where the implementation of tailored systems is limited by scant resources.
Table 1: Number of individuals using each sanitation method on water transport and
storage containers, hand washing, use of container lids and timing of their placement in
Coyoles, La Hicaca, and Lomitas during June 2011 medical brigade (N=263)
Gabriela E. Halder, MPH
Department of Medical Education, Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine, Richmond, Virginia, USA
Gonzalo Bearman, MD, MPH and Michael P. Stevens, MD, MPH
Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases and Department of Epidemiology and Infection Control, Virginia Commonwealth University Health System, Richmond, VA, USA
Kakotan Sanogo, MS
Department of Epidemiology and Infection Control, Virginia Commonwealth University Health System, Richmond, VA, USA
References
1. John V, Jain P, Rahate M, Labhasetwar P. Assessment of deterioration in water quality from source to household storage in semi-urban settings of developing countries. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 2014; 186(2): 725-734.
2. Gunnarsdottir MJ, Gardarsson SM, Elliott M, Sigmundsdottir G, Bartram J. Benefits of water safety plans: microbiology, compliance, and public health. Environmental Science & Technology 2012; 46(14): 7782-7789.
3. Trevett AF, Carter RC, Tyrrel SF. Water quality deterioration: a study of household drinking water quality in rural Honduras. International Journal of Environmental Health Research 2004; 14(4): 273-283.
4. Halder GE, Bearman G, Sanogo K, Stevens MP. Water sanitation, access, use and self-reported diarrheal disease in rural Honduras. Rural and Remote Health 13: 2413. (Online) 2013. Available: www.rrh.org.au (Accessed 7 December 2013).
5. World Health Organization. Guidelines for drinking-water quality. Vol. 1 Recommendations. 3rd edn. Geneva: WHO, 2004.


