Introduction
Suicide is common among Indigenous Peoples at a global level. While the major risk factor for suicide is a previous attempt, the reasons among children and adolescents can be attributed to the influence of sociocultural factors in the Western world1-5. It affects them disproportionately around the world, as Indigenous communities face significant structural inequalities such as marginalization, poverty, and cultural discrimination6,7. The rates of suicide among Indigenous populations are higher than in non-Indigenous youth populations2,5,6,8. Available information indicates that suicide is more common among Indigenous children and youth compared to other groups9. The psychological wellbeing of children and adolescents plays a crucial role, and achieving it is important through cohesion with the community8-12.
In Colombia, between 2010 and 2019, the suicide rate per 100,000 population ranged from 4 to 5.7 across the entire population, while among children, adolescents, and young people aged 5–19 years it ranged from 2.6 to 3.513. Suicides within Indigenous communities have been gradually increasing, increasing from 63 deaths in 2017 to 98 deaths in the 202013. For the year 2019, the regions in Colombia with the highest suicide rates were Amazonas and Vaupés, particularly among Indigenous populations13.
A study conducted with participants representing the majority of Indigenous peoples recognized in Colombia, with children, adolescents and their families, found that 89% of children and adolescents had some level of self-reported suicide risk, and parents identified this risk at 21.1% of children and young people14. They also identified that parenting practices and psychosocial difficulties in parents were associated with greater mental health disorders in children and adolescents14.
Indigenous communities face significant challenges in preserving their spiritual and cultural traditions since the period of colonization of the Americas and even more so in today's avant-garde and globalized world14. In particular, Indigenous youth and adolescents often find themselves at a point of conflict between their cultural heritage and external influences such as language, cultural belonging, technology, and the idea that progress is in the cities, which can affect emotional wellbeing and connection to cultural identity7.
Mental health for Indigenous Peoples in Colombia is understood as spiritual harmony, which is understood as a harmonious connection of the individual with spirituality, expressed in compliance and respect for the Law of Origin, in direct and harmonious relationship with the environment (territory, rivers, jungle, the universe, the four elements, and the community), which reflects strength of thought, spirit and body15,16. The mental health challenges of Indigenous Peoples and communities are due to the rupture of cultural harmony, arising from the non-compliance with cultural norms, the loss of connection with ancestral traditions, the absence of meaningful rituals, and an imbalance in the interaction with nature. This rupture is interpreted as a deviation from the path proposed by nature, and restoring it through spiritual practices and collective rituals is considered essential17. For Indigenous populations, the land is everything, ‘where the elements and plants of harmony and healing are born’ (p. 3)15.
The Embera Dobidá people mostly inhabit the Chocó rainforest. Their population is approximately 16,000 people17. In Colombia, the suicide rate was 6.2 deaths per 100,000 non-Indigenous inhabitants in 2023. At that time, the suicide rate among the Embera population was 247.9 per 100,000 individuals, with 50% of the suicides occurring among young people and adolescents13,17,18. Reports of suicidal behavior among the Embera population were non-existent 10 years ago15.
For countries affected by war, corruption, or migration, there is a significant burden of multidimensional poverty, which impacts the identity of communities and also health19-23. Approximately one million children under the age of 5 years spent their lives in conflict zones in 201924,25. For Indigenous Peoples, their land is their life, and being deprived of it represents an attack on their spirituality, beliefs, and food security14,15.
Various factors influence neurodevelopment, for example early experiences that are biologically and behaviorally integrated. This also affects subsequent generations26. Food insecurity is defined as ‘the lack of reliable access to a sufficient quantity of affordable and nutritious food’ (p. 3)27. In Colombia, an estimated 14% of children under the age of 5 years suffer from chronic malnutrition, and Chocó, in the Pacific region of Colombia, is one of the departments with the highest indicators of malnutrition27,28.
Nutritional health, mental health and territorial belonging are deeply interrelated. Good nutrition supports the brain neurochemistry necessary for emotional balance. Poor nutrition is linked to deficiencies in zinc, fatty acids, and iron, which directly relate to learning and mental health disorders in pediatric populations29. Food insecurity is associated with micronutrient deficiencies that affect the availability of building blocks for neurotransmitters involved in mood regulation30. Low low-density-lipoprotein cholesterol has been found to be associated with almost twice the risk of suicidal ideation31, suggesting that nutritional deficiencies may exacerbate depression.
In Colombia, a similar situation occurs in relation to food security inequities, with observed growth delays and nutrient deficiencies such as iron, vitamin A, and zinc deficit in children under 5 years, as well as anemic syndrome in pregnant women, these being higher than in other populations27,28. A significant cause of food insecurity is the inability to access food due to low economic levels in vulnerable populations and the malfunctioning of agrifood systems, which leads to unjustified prices28. Indigenous populations exhibit higher levels of food insecurity, with limited government response to restore their rights in most communities4-6,32.
This loss of food security, apart from the impact at a biological level, also generates an impact on the belief system and a suffering for the territory or home environment that has been called solastalgia33. Solastalgia refers to emotional or existential distress resulting from environmental change, in which a once familiar and comforting landscape becomes a source of loss and displacement33. These changes in the environment have been associated with mental health problems, especially suicidal behaviors and transgenerational psychological trauma in Colombian Indigenous communities, which contributes to the explanation of the increase in suicidal behavior in Indigenous Peoples in Latin America, especially in young people34.
The articulation between the Western healthcare system and Indigenous traditional practices is recognized as a promising strategy for enhancing mental health recovery in culturally diverse contexts. This integrative approach combines evidence-based clinical interventions (eg psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy) with ancestral healing methods that incorporate spiritual, community, and cultural components, addressing mental health in a more holistic manner. Medical literature documents that collaboration between mental health professionals and traditional healers can improve treatment acceptance, therapeutic adherence, and even clinical outcomes in Indigenous populations5,9. Global health policies recommend the inclusion of traditional healers in formal services to close the mental healthcare gap5.
The present research
The implementation of culturally appropriate nutritional interventions has demonstrated benefits in the mental health of various Indigenous communities. The sense of belonging to the territory is a crucial factor for the mental health of displaced Indigenous populations. Maintaining a strong territorial attachment provides continuity to traditions, language, and community support, acting as protection against depression and anxiety. Studies report that territorial uprooting leads to negative impacts on the psyche, while reconnecting with land and nature has therapeutic effects35. Subsistence activities (hunting, fishing, farming) undertaken after displacement can restore that sense of belonging, improving community mood and self-esteem5. Rebuilding the link with the land in displaced populations thus favors emotional resilience and recovery of wellbeing.
In many Indigenous communities, traditional foods closely linked to the land provide key nutrients (eg omega-3 fatty acids and B vitamins) that protect mental health and reinforce cultural identity27. Connection to territory facilitates access to these native foods and promotes a sense of purpose and belonging, essential factors for psychological wellbeing. This is consistent with the Indigenous holistic approach, where physical, mental, spiritual health and the relationship with the land are inseparable3,34.
Research on mental health in the Indigenous pediatric population is limited. Understanding the factors associated with spiritual disharmony or mental health issues in this group is crucial to identifying early warning signs and identifying the psychosocial factors linked to increased suicidal behavior in these communities. Similarly, understanding the impact of recovery strategies, responses to inequities, and their relationship with the Western healthcare system could highlight issues to address from the public mental health perspective with other Indigenous communities.
The objective of this study was to explore, at two time points (January 2023 and January 2025), the variables related to spiritual harmony in the Indigenous pediatric population of an Embera Dobidá community in Colombia, particularly those related to mental health, food security, general health, and connection to the land. It was also intended to determine the outcomes of strategies implemented to address these issues from the community and through their coordination with local care systems. The hypothesis suggests a relationship between food security, spiritual harmony, and family connection to the land. It was also hypothesized that traditional practices for addressing disharmony, such as healing, connecting with a new land, and culturally sensitive Western health strategies, can contribute to improved outcomes for spiritual disharmony, food insecurity, and land concerns.
Methods
This study employed a longitudinal descriptive design, structured around two data collection points (2023 and 2025). It was developed within the framework of a community-led strategy to restore spiritual harmony, co-designed by the local health directorate and the Embera Dobidá Indigenous community. The initiative began in 2023 and will continue until the end of 2025.
Study participants
The study included all children and adolescents aged 6–17 years residing in an Embera Dobidá Indigenous community displaced by armed conflict in Colombia. In 2019, 119 individuals from this community, originally from Alto Baudó–Chocó, were forcibly displaced. They resettled in a territory with no access to clean water or fishing, which affected their subsistence and wellbeing. As of 2025, the community comprised 158 members: 17.7% were children aged under 5 years, and 25.3% were aged between 6 and 16 years (the group included in this study).
Data collection process
Two data collection points were used:
- baseline (January 2023): 69 children and adolescents were assessed using the selected instruments
- follow-up (January 2025): The same participants were reassessed using the same instruments to evaluate the impact of interventions implemented between the two periods.
Inclusion criteria were being aged 6–17 years, belonging to the community, and providing informed assent alongside parental/guardian consent. No exclusion criteria were applied.
Cultural safety and identity
The principles outlined in the CONSIDER statement were followed to ensure that the strategies and data collection were culturally safe and appropriate36. One of the authors is an Indigenous leader from the community and also contributed to the design of the public health strategies and the writing of the article. The author assisted with the intercultural training of the other researchers and the pediatricians in charge of the assessment, as well as other medical students from the institution that led the research.
In this regard, it is reaffirmed that one author is the leader of the community describing the study, which meant that the community always had control over the study and the interventions carried out. Furthermore, the data belong to the community, and the community has used them to design strategies to help restore spiritual harmony. This is consistent with the First Nations Principles of Ownership, Control, Access, and Possession (https://fnigc.ca).
Strategies
Traditional ceremonies (Benecuá)
Two traditional ceremonies known as Benecuá were held, with the objective of ‘expelling the spirit of death’, according to the community's cultural practices. The first ceremony took place at the end of 2023 and the second in the course of 2024. Both were led by a Jaibaná (traditional healer) from Chocó (place of origin) and were supported by the Territorial Health Directorate of Caldas. These ceremonies included rituals of territorial cleansing and collective spiritual restoration.
Risk communication and community engagement strategy
The intervention was designed considering the key components on mental health risk communication and suicide prevention in Indigenous Peoples, which showed greater association with positive results in previous experiences. The components were mental health education, special communication plans with the community, specific actions for each territory and culture, community approach to suicidal behavior, articulation of sector and disciplines, strategies that strengthen care, and intergenerational dialog37. These components were selected for their relevance in contexts of high psychosocial vulnerability and their effectiveness in strengthening community agency, intercultural approach and collective construction of care.
Their implementation was carried out in close coordination with the traditional authorities of the Indigenous community, the primary healthcare team of the territory and the municipal mayor's office, which ensured the cultural relevance, institutional support and operational sustainability of the process. This process was developed through focus groups in the community during 2024, with the participation of stakeholders from other sectors, such as culture, sports, child protection and agriculture. This process also allowed the creation of a risk communication and community participation route for the community (Fig1).
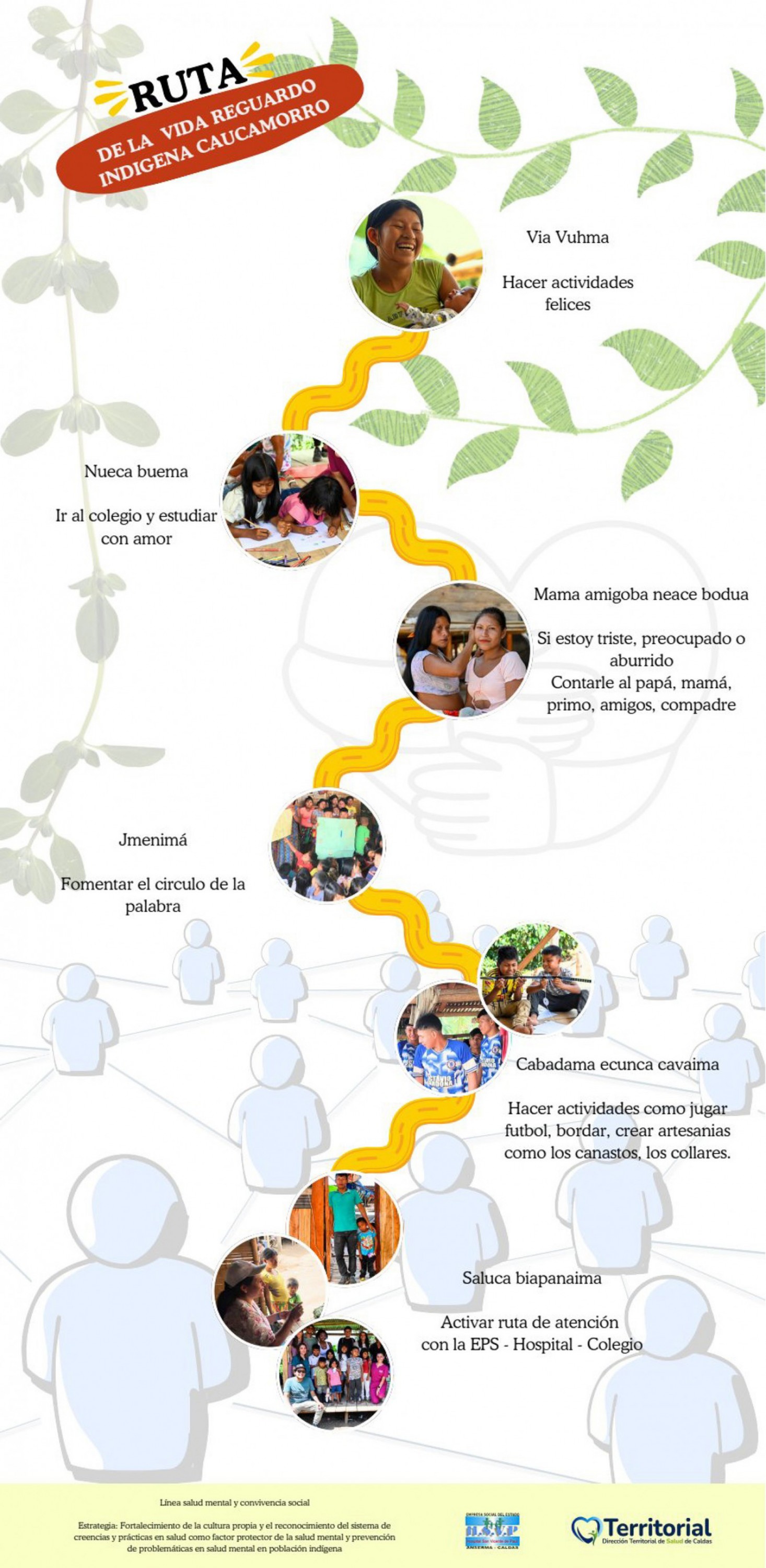 Figure 1: Life pathway model, co-created with the Embera Dobidá community of Colombia, to promote child wellbeing. Cabadama ecunca cavaima, do activities like play soccer, sew, make handcrafted objects like baskets or necklaces. Jmenimá, promote the word circle (talking circle). Nueca buema, go to school and study with love. Mama amigoba neace bodua, if i am sad, worried or bored tell mum, dad, cousin, friends or buddy. Saluca biapanaima, activate attention route with the EPS (Entidades Promotoras de Salud: health-promoting entities), hospital, school.Via vuhma, do happy activities. Source: Route of life Caucamorro Indigenous community.
Figure 1: Life pathway model, co-created with the Embera Dobidá community of Colombia, to promote child wellbeing. Cabadama ecunca cavaima, do activities like play soccer, sew, make handcrafted objects like baskets or necklaces. Jmenimá, promote the word circle (talking circle). Nueca buema, go to school and study with love. Mama amigoba neace bodua, if i am sad, worried or bored tell mum, dad, cousin, friends or buddy. Saluca biapanaima, activate attention route with the EPS (Entidades Promotoras de Salud: health-promoting entities), hospital, school.Via vuhma, do happy activities. Source: Route of life Caucamorro Indigenous community.
Psychological accompaniment with intercultural approach
A psychological support strategy was developed with an emphasis on intercultural mental health, based on the practices, knowledge and worldview of the community, led by psychology, anthropology, the community governor and a woman leader of the community. This intervention was supported by the local hospital, which facilitated the articulation with the health system in case of risks that could not be addressed in the community. This intervention included:
- cultural translation of psychological first aid into Embera
- training of an Indigenous community manager in risk management
- integration of anthropological and community methods validated by the community as appropriate for their cultural context
- strengthening of family ties and emotional management skills.
Sanitation
In coordination with the Corporación Autónoma Regional de Caldas (Corpocaldas or Regional Autonomous Corporation of Caldas), actions were implemented to improve basic sanitation and access to drinking water in the community. These measures included the installation of sanitary tanks and the supply of water with a potabilization mechanism, achieving effective coverage by mid-2024.
Assessment instruments
Culturally validated and translated instruments were used to assess mental health, food security, environmental distress, and general pediatric health. A sociodemographic survey was developed that included questions about age and gender, as well as questions that addressed ecological aspects related to migration, including ‘Do you have little access to meat, eggs and milk [protein]?’, ‘Do you miss your territory [solastalgia]?’, ‘Do you feel strange in the culture of this new place? [foreign culture]’, ‘Do you feel like you are in a foreign land?’, and ‘Do you have difficulty being near a clean river?’ Additionally, assessments were conducted by pediatricians, exploring the general health conditions. Individuals with health issues were provided with appropriate medical care pathways, including specific recommendations based on the findings.
PACES scale
The PACES scale (by its acronym in Spanish and domains: Parenting, Behavior, Emotions, and Suicide Risk) was used to assess mental health problems and suicide risk. This scale consists of 42 questions divided into two parts: one for parents and the other for children and youth aged 7–16 years38,39. It includes Likert-type response options, indicating the frequency of symptom occurrence or difficulty. This scale was designed and validated with the same Indigenous communities that participated in the study, using a participatory method, and has shown adequate measures of reliability and structural configuration. This instrument was translated into Embera in this validation process39.
Food Security Scale
The scale consisted of 12 items related to the availability of money to buy food, the reduction of meals at home due to lack of money, and the experience of hunger of any of the household members. The frequency of occurrence of each item was coded as follows: three times as ‘always’, two as ‘sometimes’, one as ‘rarely’, and zero as ‘never’. This coding allows for a food insecurity score between 0 and 36 points, from which households were classified into four categories: 0 points as ‘safe’, 1–12 points as ‘mild food insecurity’, 13–24 points as ‘food insecurity with moderate hunger’, and 25 points or more as ‘food insecurity with severe hunger’. It was validated in Colombia and showed consistency with Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations nutritional measures40,41.
Brief Solastalgia Scale
The Brief Solastalgia Scale consists of five items, with Likert-type responses for demographic variables, health, life satisfaction, climate emotion, and connection with nature. It was translated and validated in Colombia among Embera Dobidá Indigenous Peoples from Chocó, and Wayuú from La Guajira, showing adequate reliability and internal consistency. This instrument was translated into Embera in this validation process42.
Pediatric assessment
The assessment was conducted by pediatric specialists in the community at both times. Variables specific to the medical assessment were considered, including weight and height, signs of malnutrition, anemia, chronic respiratory symptoms, gastrointestinal symptoms, oral health, skin health, neurodevelopmental aspects, signs of abuse, and other general symptoms. A matrix with dichotomous variables was completed for each health condition, and the findings were subsequently aggregated. The grouping of these variables was called ‘medical problems’.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences v26 (IBM Corp; https://www.ibm.com/products/spss-statistics). Descriptive statistics were calculated (means and standard deviations), and bivariate correlations were performed to assess relationships between variables. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to evaluate changes between the two time points, and effect sizes were calculated using the r statistic.
Ethics approval
The study followed the Declaration of Helsinki. It was approved by the Indigenous community of Caucamorro, Caldas-Colombia. Approval was obtained from the community through its governor and by the Ethics Committee of the Center for Advanced Studies in Childhood and Youth, through Act 001 of February 2023. The names of the participants were kept strictly confidential. The local hospital and the municipal mayor's office were consulted to address any risks identified during the assessment process.
Results
Participants had a mean age of 14.97 years. Thirty percent of the children and adolescents evaluated presented suicidal risk and 50% manifested emotional disturbances. In addition, 20% were above the 50th percentile in the Behavioral Problems and Parental Problems scales. Relevant physical health problems were also identified (Table 1).
Statistically significant correlations (p<0.001) were identified between ecological variables, such as access to drinking water, territorial belonging and food availability; and spiritual disharmony variables, including suicidal risk, and parental and behavioral problems (Table 2). The majority of caregivers, despite having been forcibly displaced, expressed no desire to return to their original territory (95%).
In the first measurement, 97.5% of households reported a lack of food, and 77.5% stated that children sometimes go to bed hungry, while 5% do so every night. Although only 7.4% responded that there was no money to buy food, 25% of the participants indicated that they eat fewer than three times a day. In the second measurement, it is observed that, although economic conditions did not improve substantially, there was an improvement in the overall food security scores (from food insecurity with moderate hunger to mild food insecurity, in its upper range), as well as variables related to mental health, other medical findings, and environmental distress (Table 3).
The differences found between the two measurement time points of January 2023 and January 2025 reflect the impact of the strategies implemented. Statistically significant decreases were observed in PACES scores, environmental distress (solastalgia) and food insecurity. Effect sizes ranged from moderate to large between the two time points for the study variables (Table 4).
Regarding these results, the ethno-educator of the community, who was also the first person to arrive in the new place, mentioned:
In these years good things have happened. Although many have stayed, have died, have been murdered, have committed suicide, are in jail, or are living in the city ..., most of them are still here. Many already have their crops, chickens and have found rivers to fish in. Although here it is not as abundant as in Chocó, people have learned to get food. Working on farms or whatever they can find.
The children go to school, they learned to speak Spanish. I try to speak to them in Embera.
Another thing that has helped us feel better is that communication in the families has improved. We men talk more now, and they taught us to hug and say nice words to each other …
We miss Chocó. The abundance. But over their life is at risk. We feel more comfortable here now. But there is still the worry that they will move us again.
This narrative encapsulates the ambivalence of displacement, the strength of communal adaptation, and the cultural resilience underpinning recovery.
Table 1: Sociodemographic data for study participants
| Characteristic | Variable | % |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 10 | 13.2 |
| 11 |
10.3 |
|
| 12 |
1.5 |
|
| 13 |
8.8 |
|
| 14 |
4.4 |
|
| 15 |
7.4 |
|
| 16 |
5.9 |
|
| 17 |
25 |
|
| 18 |
19.1 |
|
| 19 |
4.4 |
|
| Sex | Male | 53.60 |
| Female |
46.40 |
|
| Ecological perception | Water | 6.60 |
| Protein |
66.20 |
|
| Solastalgia |
69.10 |
|
| Foreign culture |
51.7 |
|
| Foreign land |
48.50 |
|
| Medical problem | Nutritional problems | 57.40 |
| Chronic malnutrition |
57.40 |
|
| Chronic cough |
42.60 |
|
| Fever |
27.90 |
|
| Incomplete vaccination schedule |
20.60 |
|
| Scabies |
33.80 |
|
| Caries |
41.20 |
Table 2: Correlations between study variables
| Adjustment | Suicide risk | Emotions | Behavior | PACES total | BSS | Medical problems | Protein | Water | Nourishment | Solastalgia | Foreign culture | Foreign land | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bonding | –0.069 (p=0.575) | 0.054 (p=0.66) | 0.386** | 0.377** (p=0.002) | 0.574*** | 0.42** | 0.083 (p=0.501) | 0.181 (p=0.14) | 0.412*** | 0.523*** | 0.299* (p=0.013) | 0.335** (p=0.005) | 0.412*** |
| Adjustment | –0.022 (p=0.859) | 0.096 (p=0.435) | –0.131 (p=0.288) | 0.175 (p=0.153) | 0.192 (p=0.116) | 0.109 (p=0.376) | –0.045 (p=0.718) | 0.238 (p=0.05) | 0.06 (p=0.627) | 0.323** (p=0.007) | 0.337** (p=0.005) | 0.238 (p=0.05) | |
| Suicide risk | 0.366** (p=0.002) | 0.324** (p=0.007) | 0.583*** | 0.528*** | 0.702*** | 0.211 (p=0.082) | 0.686*** | 0.454*** | 0.481*** | 0.433*** | 0.686*** | ||
| Emotions | 0.774*** | 0.855*** | 0.669*** | 0.457*** | 0.172 (p=0.161) | 0.576*** | 0.536*** | 0.480*** | 0.523*** | 0.576*** | |||
| Behavior | 0.793*** | 0.618*** | 0.382** (p=0.001) | 0.282* (p=0.02) | 0.492*** | 0.612*** | 0.199 (p=0.103) | 0.245* (p=0.044) | 0.492*** | ||||
| PACES total | 0.884*** | 0.526*** | 0.272* (p=0.024) | 0.769*** | 0.716*** | 0.552*** | 0.573*** | 0.769*** | |||||
| BSS | 0.412*** | 0.148 (p=0.229) | 0.765*** | 0.617*** | 0.535*** | 0.528*** | 0.765*** | ||||||
| Medical problems | 0.415*** | 0.567*** | 0.479*** | 0.540*** | 0.504*** | 0.567*** | |||||||
| Protein | 0.12 (p=0.331) | 0.296* (p=0.014) | 0.248* (p=0.041) | 0.191 (p=0.119) | 0.12 (p=0.331) | ||||||||
| Water | 0.694*** | 0.649*** | 0.672*** | 0.879*** | |||||||||
| Nourishment | 0.397** | 0.436*** | 0.694*** | ||||||||||
| Solastalgia | 0.967*** | 0.649*** | |||||||||||
| Foreign culture | 0.672*** |
*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001
BSS, Brief Solastalgia Scale. PACES, Parenting, Behavior, Emotions, and Suicide Risk.
Table 3: Averages of the study instruments at January 2023 and January 2025
| Variable |
Mean (January 2023) |
SD |
Mean (January 2025) |
SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bonding | 1.93 | 1.633 | 1.28 | 1.144 |
| Adjustment | 2.09 | 1.751 | 1.47 | 1.376 |
| Suicide risk | 3.23 | 2.539 | 2.26 | 2.234 |
| Emotions | 2.46 | 1.731 | 1.35 | 1.076 |
| Behavior | 5.51 | 2.127 | 4.07 | 1.696 |
| PACES scale, total | 15.04 | 6.213 | 10.32 | 4.262 |
| BSS | 13.12 | 5.253 | 10.65 | 2.532 |
| Medical problems | 3.16 | 2.19 | 1.53 | 1.298 |
| Lack of money to buy food | 0.74 | 1.002 | 0.74 | 1.002 |
| An adult in the household ate less than they wanted due to a lack of money to buy food. | 0.6 | 0.995 | 0.6 | 0.995 |
| The household reduced the number of usual meals, such as skipping breakfast, lunch, or dinner due to a lack of money to buy food. | 0.21 | 0.636 | 0.21 | 0.636 |
| An adult skipped breakfast, lunch, or dinner due to a lack of money to buy food. | 0.41 | 0.674 | 0.41 | 0.674 |
| An adult ate less at the main meal because there wasn't enough food for everyone. | 1.75 | 0.76 | 1.66 | 0.66 |
| An adult complained of hunger due to a lack of food in the household. | 1.97 | 0.17 | 1.31 | 0.465 |
| An adult ate less at the main meal because there wasn't enough food for everyone. | 1.87 | 0.731 | 1.41 | 0.696 |
| Less essential food was bought for the children because there wasn't enough money. | 1.6 | 0.756 | 1.57 | 0.759 |
| A child skipped breakfast, lunch, or dinner due to a lack of money to buy food. | 0.49 | 0.837 | 0.49 | 0.837 |
| A child ate less at the main meal because there wasn't enough food for everyone. | 1.85 | 0.697 | 1.25 | 0.529 |
| A child complained of hunger due to a lack of food in the household. | 1.82 | 0.711 | 1.5 | 0.702 |
| A child went to bed hungry due to a lack of money for food. | 1.79 | 0.724 | 1.79 | 0.724 |
| Nourishment scale, total | 14.88 | 4.224 | 12.75 | 3.64 |
BSS, Brief Solastalgia Scale. PACES, Parenting, Behavior, Emotions, and Suicide Risk. SD, standard deviation.
Table 4: Effect sizes for two time points of measurement (January 2023 and January 2025) for study variables
| Statistical measure | Bonding | Adjustment | Suicide risk | Emotions | Behavior | PACES total | BSS | Medical problems | Nourishment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z† | –4.77*** | –4.377*** | –5.168*** | –5.908*** | –6.111*** | –7.126*** | –5.024*** | –5.737*** | –6.903*** |
| Effect size (r) | 0.58 | 0.63 | 0.62 | 0.72 | 0.74 | 0.86 | 0.61 | 0.69 | 0.84 |
*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001
† Wilcoxcon test.
BSS, Brief Solastalgia Scale. PACES, Parenting, Behavior, Emotions, and Suicide Risk.
Discussion
The findings of this study confirm the initial hypothesis: spiritual harmony among Indigenous children is closely linked to food security, access to clean water, physical health, and cultural connection to the land. Improvements observed in this study between 2023 and 2025 – particularly in mental health, parental bonding, and solastalgia – suggest that culturally grounded, community-driven strategies, when integrated with intercultural health actions, can significantly enhance wellbeing and reduce suicide risk.
These results are consistent with previous studies showing that suicide risk among Indigenous Peoples is shaped by historical trauma, forced displacement, and disconnection from traditional ways of life3,5,36. For example, studies among the Kuna in Panama and the Inuit in Nunavik, Canada, found strong associations between food insecurity, depressive symptoms, and internalizing behaviors in children and adolescents20,43. These findings reinforce the need to approach mental health from a broader ecological and cultural perspective, rather than from a strictly psychiatric one.
Moreover, the protective role of ancestral land, traditional food systems, and intergenerational ties has been well documented across various contexts. Community gardening programs in Canada43, and revitalized traditional diets in the Andes44 and Australia45, have all demonstrated improved mental wellbeing and strengthened cultural identity. Our study adds to this evidence by showing that reconnecting with the land – even in a new, less abundant territory – can support resilience and collective healing for displaced Indigenous families.
Importantly, this research recognizes that mental health in Indigenous worldviews is not simply the absence of psychiatric symptoms, but rather the presence of spiritual balance, relational wellbeing, and harmony with nature15,16,34. Among the Embera Dobidá, health is understood through a cosmology that distinguishes illnesses of ‘white origin’, treatable with biomedical methods, from those of spiritual origin, which require the intervention of Jaibanás or the use of medicinal plants14. Cultural practices of medicine not only address suffering but also regulate which conditions are named and treated within the community’s moral and relational frameworks43-45.
The intercultural approach adopted here – combining traditional ceremonies, adapted psychological support, and sanitation improvements – reflects a model of care rooted in reciprocity, respect, and co-construction of knowledge. In this study, the use of culturally translated psychological first aid, the involvement of a female community leader and an Indigenous governor in therapeutic processes, and the training of a local risk manager, contributed to building trust and local agency. These strategies align with international calls to decolonize mental health systems and recognize the pluriversality of healing practices.
Several limitations must be acknowledged. First, the study’s design does not allow for causal inference, as there was no control group. The interventions were part of a broader, community-led recovery process, which included both structured and spontaneous actions by the community, the local government, and the health system. This complexity makes it difficult to isolate the effect of any single component.
Second, although the instruments were culturally validated and translated into Embera, some concepts may have been partially lost due to language differences and epistemological gaps. Although translation support was provided, direct narratives from children in their own language might have yielded deeper insights. Third, the sample size reflects the size of the community itself, which limits statistical power and generalizability. However, the results are consistent with broader regional trends affecting Indigenous youth in Colombia, especially in post-conflict settings.
Furthermore, while pre- and post-intervention data were collected, the absence of a control group prevents exclusive attribution of observed changes to the implemented actions. Moreover, the biomedical framework may not fully capture the effects of collective rituals, symbolic healing, or community restoration practices. Future research should adopt longitudinal and mixed-methods designs, integrating Indigenous epistemologies and participatory approaches to better grasp the dynamics of intercultural mental health.
Despite these limitations, this study provides valuable insight into how displaced Indigenous communities can construct culturally meaningful pathways to healing. It highlights the importance of investing in intercultural health models co-designed with Indigenous authorities, recognition of spiritual disharmony as a legitimate and urgent health concern, and structural interventions addressing hunger, water scarcity, and territorial uprooting.
Future studies should examine the long-term effects of intercultural strategies, deepen understanding of environmental grief and solastalgia, and promote public health policies that uphold territorial and cultural rights as essential determinants of wellbeing.
Healing is not just a clinical goal – it is a political and spiritual process. Addressing suicide risk among Indigenous youth requires more than diagnosis; it demands restoring the conditions for buen vivir (wellbeing).
Conclusion
Spiritual disharmony – understood by many Indigenous communities in Colombia as a disruption of balance between body, territory, community, and spirit – cannot be addressed solely from a psychopathological perspective. This study shows that suicidal behavior among displaced Embera Dobidá children is linked to hunger, loss of cultural practices, war, environmental grief, and other non-psychiatric conditions.
Addressing these challenges requires recognizing the individual, familial, and collective care practices of each Indigenous community as legitimate systems of healing. It also demands that the Western health system contribute in sensitive, respectful, and dialogical ways to strengthen, rather than replace, these practices.
Only through intercultural collaboration rooted in reciprocity and epistemic humility can we begin to restore the conditions for buen vivir and ensure that Indigenous children grow up with dignity, safety, and spiritual harmony.
Acknowledgements
To the Embera Dobidá community of Caucamorro.
To Lina Valeria Cuadrado for her community perspective on mental health, to Patricia Urbina Rivera from the Territorial Health Directorate of Caldas and to María José Torres from the Municipality of Anserma, Caldas.
Funding
This work did not receive funding.
Conflicts of interest
The authors report there are no competing interests to declare. The opinions and concepts expressed in this manuscript are the sole responsibility of the authors.
Data availability statement
By community agreement, data are available upon request.


